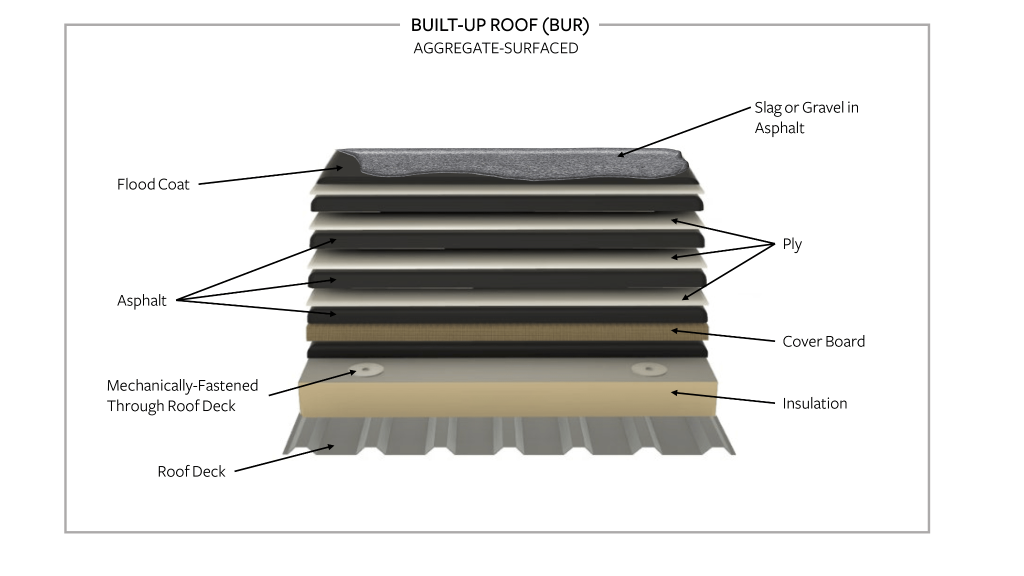
A built-up roof (BUR), also known as a tar and gravel roof, is a type of flat or low-sloped roofing system commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings. BUR roofs consist of multiple layers of reinforcing fabric (usually fiberglass or polyester) and bitumen (asphalt or coal tar) alternately layered and adhered together to create a waterproof membrane.
The construction of a BUR roof typically involves the following layers, although variations may occur depending on specific requirements:
- Base Layer: This layer is typically made of asphalt-saturated felt or fiberglass mat, serving as the base for the roofing system.
- Ply Sheets: Multiple layers of bitumen-saturated roofing felt or mats are laid over the base layer. These layers are often staggered and bonded together with hot asphalt or cold adhesive.
- Interply Bitumen: In some cases, additional layers of bitumen may be applied between the ply sheets to enhance waterproofing and reinforcement.
- Surfacing: The top layer of the BUR roof is usually a protective surfacing material, commonly gravel or mineral granules embedded in asphalt or a reflective coating. This layer protects against UV radiation, weathering, and mechanical damage.
BUR roofs are known for their durability, long lifespan, and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. They offer excellent waterproofing properties and are relatively low maintenance. However, installation can be labour-intensive and may require specialized equipment and skills.
Overall, BUR roofs have been a popular choice for flat and low-sloped roofs in commercial and industrial applications for many years, although they have become less common in residential construction due to the rise of alternative roofing materials and systems.